Skin Aging: Causes, Mechanisms, and Treatment Approaches
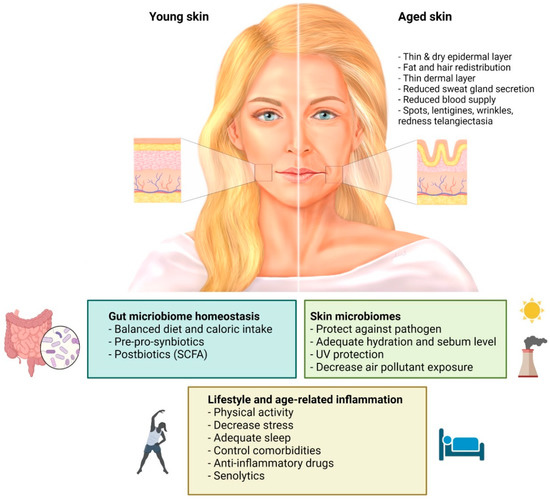
Skin aging is a multifactorial biological process influenced by intrinsic (genetic and chronological) and extrinsic (environmental) factors. It manifests as wrinkles, dryness, laxity, pigmentary changes, and thinning of the skin. As demand for anti-aging solutions grows, both topical and oral treatment approaches are being explored and marketed. However, each comes with its benefits and limitations, particularly when it comes to skin penetration and bioavailability.
Mechanisms and Causes of Skin Aging
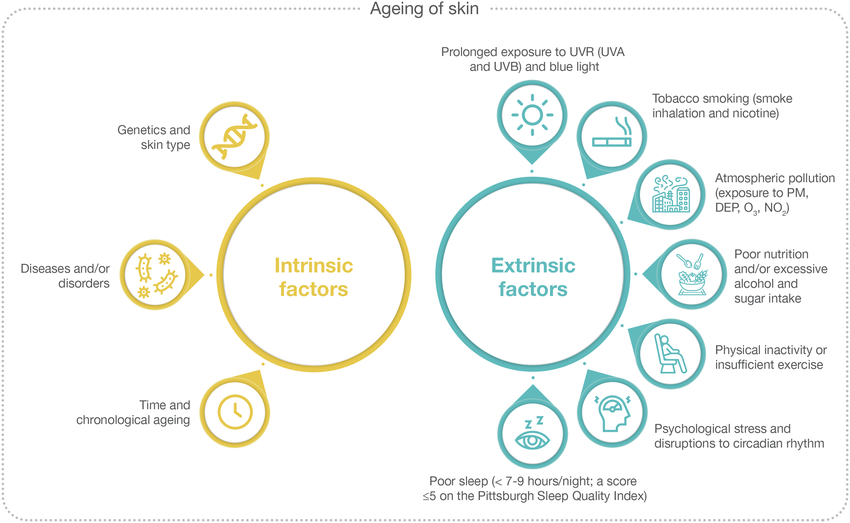
Intrinsic Aging
-
Genetically programmed and hormone-driven.
-
Characterized by reduced collagen production, thinning of the dermis, and slower cellular turnover.
-
Decreased levels of hyaluronic acid, elastin, and natural moisturizing factors.
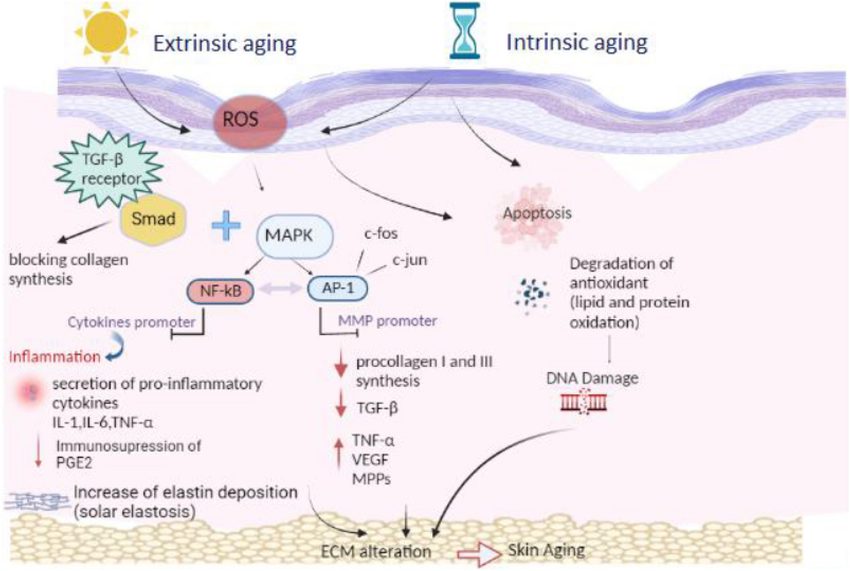
Extrinsic Aging (Photoaging)
-
Caused by UV radiation, pollution, smoking, poor diet, and stress.
-
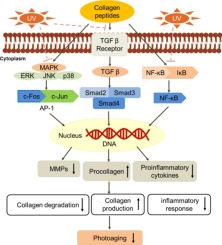
Leads to oxidative stress, DNA damage, inflammation, and breakdown of extracellular matrix (ECM) components.
-
Induces expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which degrade collagen and elastin.
Challenges of Topical Treatments
One of the major limitations of topical anti-aging products is low skin penetration. The outermost layer of the skin, the stratum corneum, acts as a strong barrier, preventing many active ingredients from reaching deeper layers where they are needed most (such as the dermis, where collagen and elastin reside).
-
Molecular size and polarity of active ingredients significantly impact penetration.
-
Lipophilic molecules penetrate more easily, but even they often struggle to reach therapeutic concentrations in deeper layers.
-
Delivery systems like liposomes, nanoemulsions, microneedles, and chemical enhancers are under development to improve efficacy.
Topical Anti-Aging Products
Despite the barrier issues, many active compounds have shown efficacy with repeated and prolonged use:
-
Retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin): Stimulate collagen production, increase cell turnover.
-
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid): Potent antioxidant, boosts collagen synthesis, evens skin tone.
-
Peptides (e.g., Matrixyl): Signal skin to produce collagen and elastin.
-
Niacinamide: Improves barrier function, reduces fine lines and hyperpigmentation.
-
Hyaluronic Acid: Moisturizes and plumps skin, though mostly affects surface layers.
-
Sunscreens: Crucial for prevention of photoaging.
Oral Anti-Aging Treatments
Oral supplements offer a systemic approach, aiming to nourish the skin from the inside out. The advantage is 100% bypass of the stratum corneum, though systemic absorption and distribution pose different challenges.
Common Oral Ingredients
Antioxidants
Including vitamins C and E, coenzyme Q10, astaxanthin, and polyphenols (from green tea, grape seed, etc.), these combat oxidative stress and inflammation, slowing ECM breakdown.
Ceramides and Essential Fatty Acids: Help improve skin hydration and barrier function from within.
Zinc, Selenium, and Biotin:
Support healthy skin regeneration and immune defense.
Human Collagen vs. Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
-
Human Collagen (oral)
-
Collagen in its native form (e.g., extracted or animal-derived) has a large molecular weight and is poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
-
It is often broken down during digestion and does not reach the skin in functional form.
Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
-
Enzymatically broken down into short peptides and amino acids for better bioavailability.
-
These peptides can stimulate fibroblast activity, increasing the body’s own collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid production.
-
Scientific studies have shown improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and reduction in wrinkles with consistent use (usually 2.5–10g/day over several weeks).
Products on the Market
Topical Products
-
Retinol-based creams (e.g., RoC Retinol Correxion, Skinceuticals Retinol)
-
Vitamin C serums (e.g., Skinceuticals CE Ferulic, La Roche-Posay Pure Vitamin C)
-
Peptide creams (e.g., The Ordinary Buffet, Olay Regenerist)
-
Moisturizers with hyaluronic acid (e.g., Neutrogena Hydro Boost, CeraVe HA Serum)
Oral Supplements
-
Collagen peptides (e.g., Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides, Verisol®, Peptan®, Naticol®)
-
Multinutrient formulas (e.g., Skinade, Imedeen, Murad Youth Builder)
-
Antioxidant blends (e.g., Astareal®, Heliocare®, Pure Encapsulations Skin Nutrients)
Future Developments and Innovations
The anti-aging field is rapidly evolving. Expected improvements include:
Enhanced Delivery Systems
-
Nanotechnology: Encapsulation of active ingredients in nano-sized carriers for deeper skin penetration.
-
Microneedles and dissolvable patches: For transdermal delivery of peptides and growth factors.
Smart Personalization
-
DNA-based skin analysis and microbiome testing to tailor treatments to individual skin needs.
-
AI-powered skincare recommendations.
Bioactive Peptides and Growth Factors
-
Synthetic and biomimetic peptides that can target specific receptors in the skin for collagen stimulation and skin repair.
Advanced Oral Formulations
-
Postbiotics and collagen-boosting cofactors in combination (e.g., vitamin C, zinc).
-
Targeted delivery capsules that release nutrients in the small intestine for optimized absorption.
-